Our Solution
|
Closed Loop Dosing
Sanso's on-board technology will automatically adjust oxygen dosing in real-time based on pulse oximetry readings, yet users can still manually boost the oxygen supply in anticipation of demand or switch to continuous flow at any time. Closed Loop Monitoring Sanso's cloud-based service connects patients, providers, and payers. While there are many options to make oxygen therapy more portable, convenient, and efficient for the patient, none have addressed the true problem: the failure to close the loop between the prescribed drug therapy (oxygen), a desired clinical measurement (oxygen saturation rate), patient outcome (better oxygenation), and cost-reduction (fewer exacerbations and hospitalizations). |
The a original algorithm helped to solve this problem when it resulted in the creation of the first FDA cleared closed-loop feedback control system. Sanso is now developing the second generation systems, the Sanso Via and the Sanso Versa, which will provide real-time data collection and immediate therapeutic adjustments, thus helping to improve patient outcomes.
Simply put, the Sanso Via system delivers as much oxygen as needed, but only when it is actually needed.
Smart RegulatorSmall and lightweight regulator fits standard oxygen tanks and includes real-time recording and wireless transmission of respiration rate, oxygen saturation, pulse rate, and oxygen consumption.
|
AlgorithmSanso's oxygen optimization algorithm auto-titrates using industry standard pulse oximetry on the ear or finger. The second generation system is currently under development
|
Real-Time MonitoringData collected can be programmed for automatic wireless transmission to the Cloud. Caregivers can set parameters and frequency of transmissions and integrate data with existing care management applications and EMR systems.
|
The dynamic capabilities of the Sanso Via can help enable providers to improve blood oxygen saturation at every moment of care
- Patient outcomes can be improved as they receive a boost of O2 only when SpO2 level drops below level set by their provider
- Hospital readmissions can be prevented as patients become more active in response to improved therapy at home
- ER visits can be prevented as the Sanso Via system connects to healthcare providers who are notified of problems, or when the system is not being worn, so they can intervene as needed
- Oxygen costs can be reduced as oxygen is consumed by the patient only when it is actually needed
- Secure wireless transmission of patient vital signs can help clinicians better determine appropriate drugs and therapy remotely
|
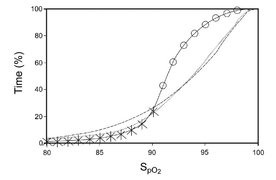
Sanso Via works to prevent both hypoxia (under-oxygenation) and hyperoxia (over-oxygenation). Hypoxia is frequently encountered in COPD and is responsible for a reduction in exercise tolerance and causes severe complications. Patients’ needs are variable and episodes of oxygen desaturation may occur during daily activities, despite the use of oxygen therapy. By adjusting the oxygen dose automatically, research shows patients will spend more time within the desired SpO2 range as well as experience fewer hypoxic events [M. G. Iobbi, 2007]. In addition, one study showed a 50% decrease in oxygen delivered without a significant increase in the time of desaturation [Z. Zhu, 2005].
Concerns over hyperoxia have led to research including a new trial that suggests supplemental oxygen therapy in patients with ST-elevation MI (STEMI) may actually be harmful for patients who are not hypoxic [Stub, 2015]. The Air Versus Oxygen in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (AVOID) trial compared supplemental oxygen versus no oxygen unless O2 fell below 94%. Results of the AVOID study showed that providing supplemental oxygen therapy in these patients may increase early myocardial injury and was associated with larger myocardial infarct size assessed at six months. They also found an increase in the rate of recurrent myocardial infarction and an increase in frequency of cardiac arrhythmia in the oxygen group. The AVOID study investigators would really question the current practice of giving oxygen to all patients and certainly to those who have normal oxygen levels to begin with. Austin and colleagues compared high flow oxygen versus titrated oxygen treatment in a group of patients with COPD exacerbation in Tasmania [Austin MA, 2010]. They evaluated 214 patients with a diagnosis of COPD exacerbation, of whom 117 received high flow oxygen and 97 received titrated oxygen therapy. In this group the mortality was 9% in the high flow oxygen group, and 2% in the titrated oxygen group. Patients receiving titrated oxygen were far less likely to have acidosis or hypercapnia. Despite the recommendations, it has been shown that the vast majority of patients hospitalized for exacerbations of chronic respiratory disease receive oxygen at high flows. Data strongly suggests a reversal is needed regarding the use of high flow oxygen in acute care settings in favor of auto-titrating to SpO2 levels. |